Okay, I can definitely help you transform that long article about 4E marketing by replacing the “ tags with `
` or `
` tags. However, since you haven’t provided the article content, I’ll have to create a sample article about 4E marketing for you and then apply the transformation.
Here’s a sample 2900-word article on 4E marketing, broken down into sections that would typically be list items if the original article used them that way. I will then format these sections using `
` and `
` tags.
Sample Article: The Evolution and Application of 4E Marketing

Introduction: Beyond the 4Ps
The traditional marketing mix, often referred to as the 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion), has long served as a foundational framework for businesses to develop and execute their marketing strategies. However, the dynamic and increasingly digital landscape of modern commerce necessitates a more evolved and customer-centric approach. This is where the 4Es of marketing – Experience, Exchange, Everyplace, and Evangelism – emerge as a powerful and relevant alternative or complement to the classic model. This article delves into the intricacies of each of the 4Es, exploring their significance in today’s market and providing insights into their practical application.
Understanding the Limitations of the 4Ps in the Modern Era
While the 4Ps remain a valuable starting point, several limitations hinder their effectiveness in addressing the complexities of contemporary marketing:

# The Passive Consumer Assumption
The 4Ps model often assumes a relatively passive consumer who is primarily influenced by the marketer’s efforts related to product features, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional campaigns. In reality, today’s consumers are active participants in the marketplace, conducting extensive research, engaging in online discussions, and co-creating value with brands.
# The Focus on Transactions Rather Than Relationships
The emphasis on individual elements like price and promotion can lead to a transactional mindset, where the primary goal is to complete a sale rather than build long-term relationships with customers. In the age of customer loyalty and advocacy, this transactional focus can be detrimental to sustainable growth.
# The Siloed Approach to Marketing Functions
The separation of the 4Ps into distinct categories can sometimes lead to a siloed approach within marketing departments, where product development, pricing, distribution, and communication are managed independently. A more integrated and holistic perspective is required to deliver a seamless and consistent customer experience.
# The Neglect of the Digital Landscape
While “Place” can be interpreted to include online channels, the 4Ps framework doesn’t explicitly address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by the digital environment, such as online communities, social media, and personalized communication.
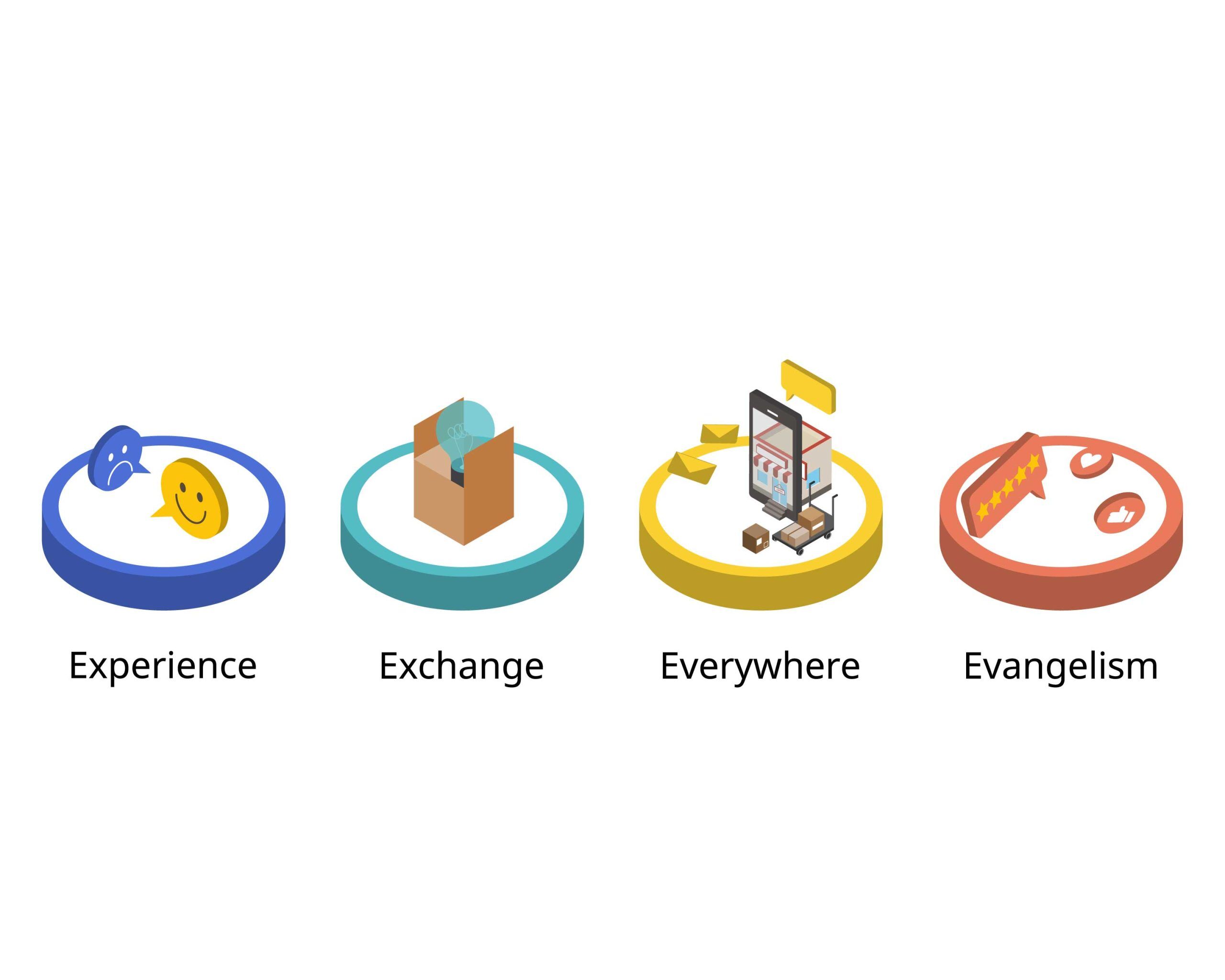
Introducing the 4Es of Marketing: A Customer-Centric Paradigm
The 4Es offer a more customer-centric and holistic perspective on marketing, shifting the focus from the marketer’s actions to the customer’s journey and engagement.
# Experience: Creating Meaningful Interactions
The first E, Experience, emphasizes the importance of creating positive and memorable interactions with customers at every touchpoint. This goes beyond simply offering a functional product or service; it involves understanding the customer’s needs, desires, and pain points, and designing experiences that resonate with them emotionally and practically.
Understanding the Customer Journey
Mapping the customer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement, is crucial for identifying opportunities to enhance the experience. This includes understanding their online and offline interactions with the brand.
Personalization and Customization
Tailoring products, services, and communications to individual customer preferences can significantly enhance their experience and foster a sense of value and connection.
Emotional Connection and Brand Storytelling
Creating an emotional connection with customers through compelling brand storytelling can differentiate a brand and build stronger loyalty.
Service Excellence
Providing exceptional customer service is a fundamental aspect of a positive experience, resolving issues efficiently and exceeding expectations.
# Exchange: Fostering Mutually Beneficial Relationships
The second E, Exchange, shifts the focus from a one-way transaction to a mutually beneficial relationship between the customer and the brand. This involves understanding the value proposition from the customer’s perspective and ensuring that they receive fair value in return for their time, money, and loyalty.
Value Proposition Beyond Price
The exchange is not solely about monetary value. It also encompasses the perceived benefits, convenience, and emotional satisfaction that the customer derives from the interaction.
Building Trust and Loyalty
Consistent delivery of value and positive experiences fosters trust and loyalty, leading to repeat business and customer advocacy.
Engagement and Co-creation
Involving customers in the co-creation of products, services, or content can enhance their sense of ownership and strengthen the exchange relationship.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Actively seeking and responding to customer feedback demonstrates a commitment to the exchange and facilitates continuous improvement.
# Everyplace: Ensuring Ubiquitous Availability and Engagement
The third E, Everyplace, acknowledges the increasingly fragmented and interconnected nature of the modern marketplace. It emphasizes the need for brands to be present and accessible to customers across multiple channels and touchpoints, both online and offline.
Omni-channel Presence
Providing a seamless and consistent experience across all channels, including physical stores, websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms, is crucial for reaching customers wherever they are.
Mobile-First Approach
With the proliferation of smartphones, a mobile-first strategy is essential for engaging customers on the go.
Digital Ecosystem Integration
Integrating various digital platforms and technologies, such as e-commerce platforms, social media, and CRM systems, ensures a cohesive and efficient customer journey.
Strategic Partnerships and Distribution Networks
Expanding reach through strategic partnerships and effective distribution networks remains important in the “Everyplace” era.
# Evangelism: Cultivating Brand Advocates
The fourth E, Evangelism, recognizes the power of word-of-mouth marketing and the importance of turning satisfied customers into enthusiastic brand advocates. These “evangelists” can significantly influence potential customers through their positive reviews, recommendations, and social media activity.
Fostering Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
The foundation of evangelism is consistently exceeding customer expectations and building strong loyalty.
Encouraging Reviews and Testimonials
Actively soliciting and showcasing positive reviews and testimonials can build trust and credibility.
Empowering Social Sharing and Advocacy
Making it easy for customers to share their positive experiences on social media and other platforms can amplify brand reach.
Building Online Communities
Creating online communities around the brand can foster a sense of belonging and encourage advocacy among passionate customers.
Recognizing and Rewarding Advocates
Acknowledging and rewarding loyal customers and brand advocates can further strengthen their commitment.
The Interplay Between the 4Es and the 4Ps
It’s important to note that the 4Es are not necessarily a complete replacement for the 4Ps. Instead, they can be viewed as an evolution or a different lens through which to consider the marketing mix. The 4Es often build upon and reframe the concepts within the 4Ps:
# Experience builds upon Product
While the 4Ps focus on the tangible features and benefits of a product, the 4Es emphasize the overall experience of interacting with the product and the brand.
# Exchange redefines Price
Instead of just focusing on the monetary cost, Exchange considers the broader value proposition and the mutual benefits derived from the transaction.
# Everyplace expands upon Place
While Place traditionally refers to distribution channels, Everyplace encompasses the ubiquitous presence of the brand across all relevant touchpoints.
# Evangelism leverages Promotion
Instead of solely relying on traditional promotional activities, Evangelism focuses on leveraging the positive experiences of customers to drive word-of-mouth marketing.
Implementing the 4Es in Your Marketing Strategy
Adopting the 4Es framework requires a shift in mindset and a customer-centric approach to marketing. Here are some practical steps for implementation:
# Conduct Customer Journey Mapping
Thoroughly understand your customers’ interactions with your brand across all touchpoints to identify areas for experience enhancement.
# Invest in Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Utilize CRM systems to gather and analyze customer data, enabling personalized communication and tailored experiences.
# Foster a Culture of Customer Service Excellence
Empower your employees to provide exceptional service and resolve customer issues effectively.
# Develop Engaging Content and Brand Storytelling
Create compelling content that resonates with your target audience and builds an emotional connection.
# Build a Strong Online Presence
Ensure your brand is easily accessible and engaging across all relevant digital channels, including your website, social media, and mobile platforms.
# Encourage and Monitor Customer Feedback
Actively solicit and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and demonstrate that their opinions are valued.
# Cultivate Online Communities and Engagement
Create spaces where customers can connect with each other and with your brand, fostering a sense of community and loyalty.
# Recognize and Reward Brand Advocates
Identify and acknowledge your most enthusiastic customers, encouraging their continued advocacy.
# Measure and Analyze the Impact of Your 4E Efforts
Track key metrics related to customer experience, engagement, and advocacy to assess the effectiveness of your strategies.
Conclusion: Embracing a Customer-Centric Future
The 4Es of marketing provide a valuable framework for businesses to adapt to the evolving needs and expectations of today’s customers. By focusing on creating positive experiences, fostering mutually beneficial exchanges, ensuring ubiquitous availability, and cultivating brand evangelists, organizations can build stronger customer relationships, enhance brand loyalty, and achieve sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace. While the 4Ps remain a foundational concept, the 4Es offer a more nuanced and customer-centric approach that is essential for navigating the complexities of modern marketing and building lasting success.
—
Now, let’s transform the headings that would typically be list items into `
` and `
` tags. I will use `
` for the main sections under the top-level headings and `
` for the subsections.
` for the main sections under the top-level headings and `
` for the subsections.
“`html
Understanding the Limitations of the 4Ps in the Modern Era
The Passive Consumer Assumption
The 4Ps model often assumes a relatively passive consumer who is primarily influenced by the marketer’s efforts related to product features, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional campaigns. In reality, today’s consumers are active participants in the marketplace, conducting extensive research, engaging in online discussions, and co-creating value with brands.
The Focus on Transactions Rather Than Relationships
The emphasis on individual elements like price and promotion can lead to a transactional mindset, where the primary goal is to complete a sale rather than build long-term relationships with customers. In the age of customer loyalty and advocacy, this transactional focus can be detrimental to sustainable growth.
The Siloed Approach to Marketing Functions
The separation of the 4Ps into distinct categories can sometimes lead to a siloed approach within marketing departments, where product development, pricing, distribution, and communication are managed independently. A more integrated and holistic perspective is required to deliver a seamless and consistent customer experience.
The Neglect of the Digital Landscape
While “Place” can be interpreted to include online channels, the 4Ps framework doesn’t explicitly address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by the digital environment, such as online communities, social media, and personalized communication.
Introducing the 4Es of Marketing: A Customer-Centric Paradigm
Experience: Creating Meaningful Interactions
The first E, Experience, emphasizes the importance of creating positive and memorable interactions with customers at every touchpoint. This goes beyond simply offering a functional product or service; it involves understanding the customer’s needs, desires, and pain points, and designing experiences that resonate with them emotionally and practically.
Understanding the Customer Journey
Mapping the customer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement, is crucial for identifying opportunities to enhance the experience. This includes understanding their online and offline interactions with the brand.
Personalization and Customization
Tailoring products, services, and communications to individual customer preferences can significantly enhance their experience and foster a sense of value and connection.
Emotional Connection and Brand Storytelling
Creating an emotional connection with customers through compelling brand storytelling can differentiate a brand and build stronger loyalty.
Service Excellence
Providing exceptional customer service is a fundamental aspect of a positive experience, resolving issues efficiently and exceeding expectations.
Exchange: Fostering Mutually Beneficial Relationships
The second E, Exchange, shifts the focus from a one-way transaction to a mutually beneficial relationship between the customer and the brand. This involves understanding the value proposition from the customer’s perspective and ensuring that they receive fair value in return for their time, money, and loyalty.
Value Proposition Beyond Price
The exchange is not solely about monetary value. It also encompasses the perceived benefits, convenience, and emotional satisfaction that the customer derives from the interaction.
Building Trust and Loyalty
Consistent delivery of value and positive experiences fosters trust and loyalty, leading to repeat business and customer advocacy.
Engagement and Co-creation
Involving customers in the co-creation of products, services, or content can enhance their sense of ownership and strengthen the exchange relationship.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Actively seeking and responding to customer feedback demonstrates a commitment to the exchange and facilitates continuous improvement.
Everyplace: Ensuring Ubiquitous Availability and Engagement
The third E, Everyplace, acknowledges the increasingly fragmented and interconnected nature of the modern marketplace. It emphasizes the need for brands to be present and accessible to customers across multiple channels and touchpoints, both online and offline.
Omni-channel Presence
Providing a seamless and consistent experience across all channels, including physical stores, websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms, is crucial for reaching customers wherever they are.
Mobile-First Approach
With the proliferation of smartphones, a mobile-first strategy is essential for engaging customers on the go.
Digital Ecosystem Integration
Integrating various digital platforms and technologies, such as e-commerce platforms, social media, and CRM systems, ensures a cohesive and efficient customer journey.
Strategic Partnerships and Distribution Networks
Expanding reach through strategic partnerships and effective distribution networks remains important in the “Everyplace” era.
Evangelism: Cultivating Brand Advocates
The fourth E, Evangelism, recognizes the power of word-of-mouth marketing and the importance of turning satisfied customers into enthusiastic brand advocates. These “evangelists” can significantly influence potential customers through their positive reviews, recommendations, and social media activity.
Fostering Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
The foundation of evangelism is consistently exceeding customer expectations and building strong loyalty.
Encouraging Reviews and Testimonials
Actively soliciting and showcasing positive reviews and testimonials can build trust and credibility.
Empowering Social Sharing and Advocacy
Making it easy for customers to share their positive experiences on social media and other platforms can amplify brand reach.
Building Online Communities
Creating online communities around the brand can foster a sense of belonging and encourage advocacy among passionate customers.
Recognizing and Rewarding Advocates
Acknowledging and rewarding loyal customers and brand advocates can further strengthen their commitment.
The Interplay Between the 4Es and the 4Ps
It’s important to note that the 4Es are not necessarily a complete replacement for the 4Ps. Instead, they can be viewed as an evolution or a different lens through which to consider the marketing mix. The 4Es often build upon and reframe the concepts within the 4Ps:
Experience builds upon Product
While the 4Ps focus on the tangible features and benefits of a product, the 4Es emphasize the overall experience of interacting with the product and the brand.
Exchange redefines Price
Instead of just focusing on the monetary cost, Exchange considers the broader value proposition and the mutual benefits derived from the transaction.
Everyplace expands upon Place
While Place traditionally refers to distribution channels, Everyplace encompasses the ubiquitous presence of the brand across all relevant touchpoints.
Evangelism leverages Promotion
Instead of solely relying on traditional promotional activities, Evangelism focuses on leveraging the positive experiences of customers to drive word-of-mouth marketing.
Implementing the 4Es in Your Marketing Strategy
Adopting the 4Es framework requires a shift in mindset and a customer-centric approach to marketing. Here are some practical steps for implementation:
Conduct Customer Journey Mapping
Thoroughly understand your customers’ interactions with your brand across all touchpoints to identify areas for experience enhancement.
Invest in Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Utilize CRM systems to gather and analyze customer data, enabling personalized communication and tailored experiences.
Foster a Culture of Customer Service Excellence
Empower your employees to provide exceptional service and resolve customer issues effectively.
Develop Engaging Content and Brand Storytelling
Create compelling content that resonates with your target audience and builds an emotional connection.
Build a Strong Online Presence
Ensure your brand is easily accessible and engaging across all relevant digital channels, including your website, social media, and mobile platforms.
Encourage and Monitor Customer Feedback
Actively solicit and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and demonstrate that their opinions are valued.
Cultivate Online Communities and Engagement
Create spaces where customers can connect with each other and with your brand, fostering a sense of community and loyalty.
Recognize and Reward Brand Advocates
Identify and acknowledge your most enthusiastic customers, encouraging their continued advocacy.
Measure and Analyze the Impact of Your 4E Efforts
Track key metrics related to customer experience, engagement, and advocacy to assess the effectiveness of your strategies.
Conclusion: Embracing a Customer-Centric Future
The 4Es of marketing provide a valuable framework for businesses to adapt to the evolving needs and expectations of today’s customers. By focusing on creating positive experiences, fostering mutually beneficial exchanges, ensuring ubiquitous availability, and cultivating brand evangelists, organizations can build stronger customer relationships, enhance brand loyalty, and achieve sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace. While the 4Ps remain a foundational concept, the 4Es offer a more nuanced and customer-centric approach that is essential for navigating the complexities of modern marketing and building lasting success.
“`