The Rise of digital Dental Sensors: Revolutionizing Oral Healthcare
In the ever-evolving field of dentistry, technological advancements continue to reshape the way oral healthcare is delivered. Among these innovations, digital dental sensors have emerged as a cornerstone, transforming diagnostic capabilities and enhancing patient care. This article delves into the intricacies of digital dental sensors, exploring their principles, benefits, applications, and the profound impact they have on modern dentistry.
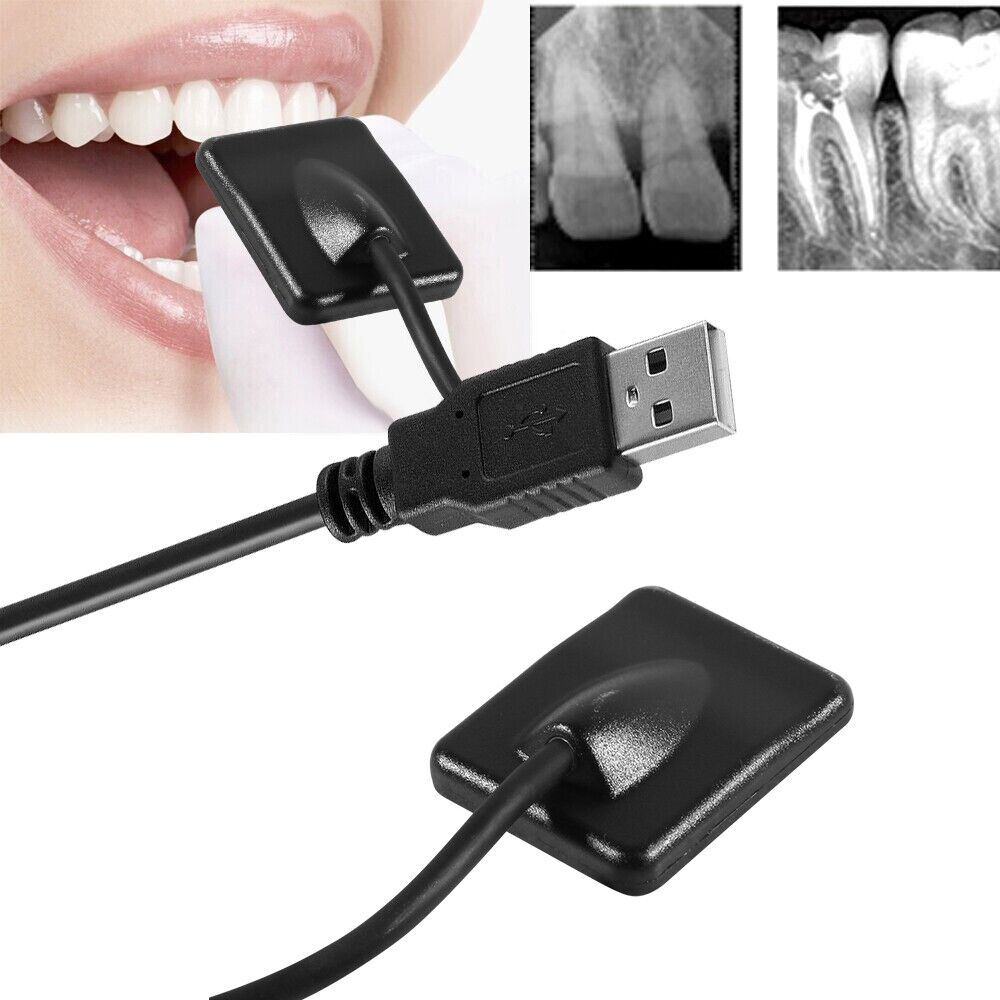
Digital dental sensors are electronic devices that capture and convert X-ray images into digital format. Unlike traditional film-based radiography, which requires manual processing and development, digital sensors provide instant, high-resolution images on a computer screen. This real-time feedback empowers dentists with crucial diagnostic information, enabling them to make informed decisions about patient treatment.
1. Sensor Chip:
This is the core component, comprised of millions of tiny pixels that convert X-ray energy into electrical signals. The quality of the sensor chip significantly influences image resolution and sensitivity.
2. Connecting Cable:
This cable transmits the electrical signals from the sensor chip to the computer.
3. Sensor Housing:

This protective casing houses the sensor chip and electronics, ensuring durability and ease of use.
1. Charged Coupled Device (CCD) Sensors:
These sensors utilize a semiconductor chip to capture and store the X-ray image. CCD sensors are known for their high sensitivity and excellent image quality.
2. Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) Sensors:
CMOS sensors are becoming increasingly popular due to their lower cost, smaller size, and lower power consumption. They offer comparable image quality to CCD sensors while being more durable and robust.
1. X-ray Exposure: The dentist positions the sensor in the patient’s mouth and takes an X-ray.
2. Signal Conversion: The sensor chip converts the X-ray energy into electrical signals.
3. Data Transmission: The electrical signals are transmitted to the computer via the connecting cable.
4. Image Processing: The computer software processes the digital data and displays the image on the screen.
Superior Image Quality: Digital sensors produce high-resolution images with excellent contrast and detail, allowing for more precise diagnosis of dental conditions.
Elimination of Darkroom Procedures: Digital sensors eliminate the need for film processing, darkroom equipment, and chemicals, streamlining the workflow and reducing overhead costs.
Increased Comfort: Digital sensors are often thinner and more comfortable for patients than traditional film.
Digital dental sensors are used in a wide range of dental procedures, including:
Cavity Detection: Identifying early signs of tooth decay.
Continued advancements in technology are driving the evolution of digital dental sensors. Future developments may include:
Wireless Sensors: Eliminating the need for connecting cables, enhancing flexibility and ease of use.
Digital dental sensors have revolutionized the field of dentistry, offering numerous advantages over traditional film-based radiography. By providing high-resolution images, reducing radiation exposure, and improving workflow efficiency, digital sensors have become an indispensable tool for modern dental practices. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative solutions to emerge, further enhancing the quality of oral healthcare.